Inflammation is a buzzword that’s often thrown around in health conversations, but what does it really mean? While your body naturally uses inflammation as a defense mechanism to fight off infections and injuries, chronic inflammation can lead to serious health issues like heart disease, arthritis, and even certain cancers. The good news? You have more control over this than you might think. One of the most powerful tools at your disposal is your diet.
In our fast-paced world filled with processed foods and sugary snacks, it’s easy for unhealthy eating habits to creep in without us even noticing. But by making mindful dietary choices, we can take significant steps toward reducing inflammation and improving overall well-being. Ready to discover how simple changes on your plate could lead to big benefits for your health? Let’s dive into the dynamic relationship between diet and inflammation!
Understanding Inflammation: What It Is and Why It Matters
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to protect itself. When you get injured or encounter harmful pathogens, your immune system kicks in, triggering inflammation. This process is meant to heal tissues and fend off invaders.
However, not all inflammation is beneficial. Chronic inflammation can linger long after the initial threat has passed. It may occur due to factors like stress, poor diet, or environmental toxins.
This persistent state puts extra strain on organs and systems within your body. Over time, it can contribute to various health issues such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders.
Understanding this delicate balance between necessary defense mechanisms and harmful chronic conditions is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Recognizing the signs early on can empower you to take proactive steps toward improvement through lifestyle changes.
The Role of Diet in Inflammation
Diet plays a significant role in inflammation. What we eat directly influences our body’s inflammatory responses. Certain foods can trigger or exacerbate these reactions, while others help soothe them.
For instance, foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates often lead to increased inflammation. Processed snacks and sugary beverages can contribute to chronic health issues over time.
On the other hand, nutrient-rich foods provide essential vitamins and antioxidants that combat inflammation. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and healthy fats are key players in this battle.
The balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is crucial too. Too much omega-6 from processed oils can promote inflammation while omega-3s found in fish counteract it effectively.
Choosing whole food sources over highly processed options not only supports overall health but also creates a more balanced inflammatory response within the body.
Foods That Increase Inflammation
Certain foods can contribute to inflammation in the body, making it essential to recognize them. Processed sugars are among the top culprits. They not only spike blood sugar levels but also trigger a cascade of inflammatory responses.
Trans fats are another significant offender. Found in some margarine and fast food, they have been linked to increased markers of inflammation. These unhealthy fats disrupt cellular function and promote heart disease.
Refined carbohydrates like white bread and pastries may seem harmless, yet they can elevate insulin levels rapidly—resulting in inflammation over time.
Additionally, excessive consumption of red and processed meats has shown associations with chronic inflammatory conditions. The compounds formed during cooking these meats can exacerbate immune responses.
Though dairy is nutritious for many, it may provoke symptoms in those sensitive or intolerant to lactose or casein, leading to discomfort and swelling within the body.
Foods That Reduce Inflammation
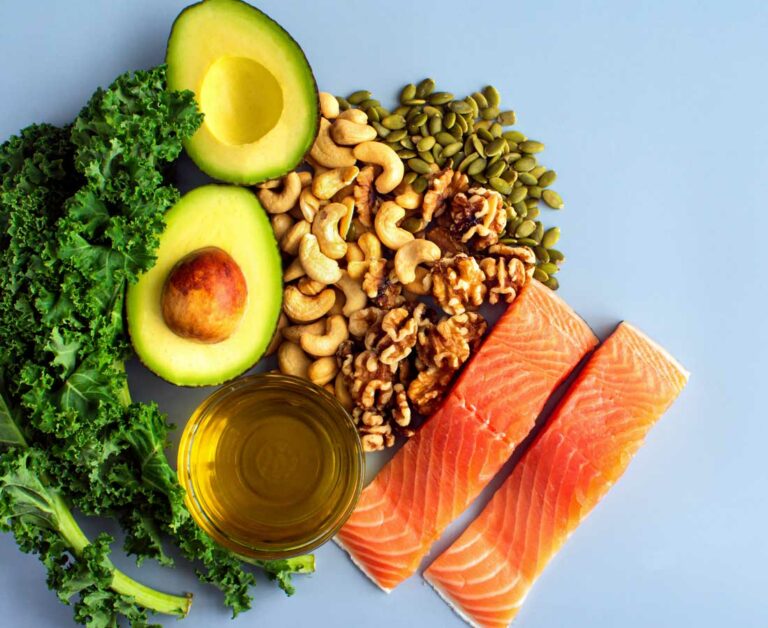
Incorporating certain foods into your diet can be a powerful way to combat inflammation. Leafy greens like spinach and kale are packed with antioxidants, which help fight oxidative stress in the body.
Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats have been shown to lower inflammatory markers significantly.
Berries also play a crucial role. Blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries contain compounds that reduce inflammation at the cellular level.
Spices shouldn’t be overlooked either. Turmeric contains curcumin, known for its potent anti-inflammatory properties. A pinch of this golden spice can transform both flavor and health benefits.
Olive oil is another excellent choice. Extra virgin olive oil provides heart-healthy fats along with anti-inflammatory effects comparable to those of ibuprofen according to research findings.
Adding these foods regularly can make a noticeable difference in overall health while managing inflammation effectively.
Creating an Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan
Designing an anti-inflammatory meal plan can be both enjoyable and rewarding. Start by incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables. These are packed with antioxidants, which help combat inflammation.
Focus on whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats instead of processed options. They provide lasting energy without spiking blood sugar levels.
Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish such as salmon or sardines are particularly beneficial for reducing inflammation.
Don’t forget to add herbs and spices to your meals; turmeric and ginger are excellent choices known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Aim for balance in each meal—combine protein, fiber-rich carbohydrates, and healthy fats to keep you satisfied while nourishing your body effectively.
Incorporating Exercise and Stress Management for Optimal Results
Exercise and stress management are key players in the battle against inflammation. Physical activity boosts circulation, delivering essential nutrients throughout your body. It also helps regulate inflammatory markers, keeping them in check.
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine doesn’t mean you need to hit the gym daily. A brisk walk, yoga classes, or even dancing can work wonders for both body and mind. Aim for at least 30 minutes most days of the week to reap maximum benefits.
Managing stress is equally important. Chronic stress can trigger inflammation, so finding effective techniques is crucial. Mindfulness practices like meditation or deep breathing exercises help calm the mind and reduce tension.
Combining these strategies with a healthy diet enhances your overall health profile. The synergy between movement and mental well-being fosters an environment where inflammation struggles to thrive, paving the way for a healthier you.
Making Small Changes for Big Benefits in Reducing Inflammation
Making small changes in your diet can lead to significant improvements in reducing inflammation. Start by incorporating more whole foods into your meals. Fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats should take center stage on your plate.
Even minor adjustments can have a big impact. Swap out refined sugars for natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup. Choose olive oil instead of vegetable oils when cooking. These simple swaps help reduce inflammatory responses in the body.
Focus on gradual transitions rather than drastic overhauls. This makes it easier to stick with your new eating habits long-term. For example, if you’re used to eating red meat frequently, try replacing one meal each week with plant-based protein sources such as lentils or chickpeas.
Remember that hydration is also vital for health and inflammation reduction. Drinking plenty of water helps flush out toxins from the body and supports overall health.
Incorporating these small dietary changes can pave the way for a healthier lifestyle focused on reducing inflammation naturally through diet choices you enjoy making every day!