Introduction to Biometric Security
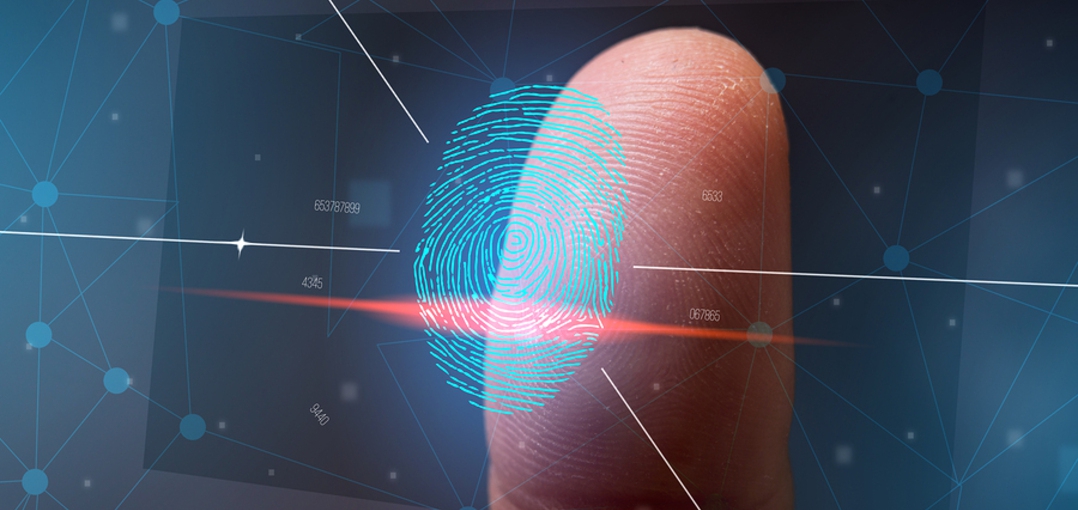
Biometric security is revolutionizing the way we protect our digital lives. Imagine unlocking your phone with just a glance or a fingerprint. It’s convenient and fast, but at what cost? As technology advances, biometric authentication has become more prevalent in our daily routines. From smartphones to secure access points, this cutting-edge method offers both ease of use and potential risks.
But before you embrace the latest tech trend, it’s important to understand what biometric security truly entails. The balance between convenience and safety raises critical questions about privacy and data protection. Let’s dive deeper into the world of biometrics—exploring its various technologies, advantages, disadvantages, and what it means for your personal information in an ever-connected society.
Types of Biometric Technologies
Biometric technologies come in various forms, each harnessing unique biological traits for identification.
Fingerprint recognition is perhaps the most well-known. This method scans and matches patterns on an individual’s fingertips. It’s widely used in smartphones and security systems due to its accuracy and speed.
Facial recognition takes a different approach. By analyzing facial features, this technology identifies individuals from images or video feeds. It’s gaining traction in both personal devices and public surveillance systems.
Iris scanning offers another layer of precision. It examines the unique patterns within the colored part of the eye, making it one of the most secure methods available.
Voice recognition leverages vocal qualities for authentication. This form captures distinctive speech patterns to verify identity, often seen in virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa.
Behavioral biometrics analyze user habits such as typing speed or mouse movements, adding yet another dimension to biometric authentication strategies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Biometric Security
Biometric security offers remarkable advantages. It enhances user convenience by providing quick access to devices and systems without the need for passwords. This technology is hard to replicate, making unauthorized entry significantly more difficult.
However, it’s not all positive. One major disadvantage lies in its susceptibility to data breaches. If biometric data gets compromised, it cannot be changed like a password can.
Moreover, the technology requires sophisticated hardware that may not always be available or affordable for everyone. User acceptance can also vary; some individuals feel uneasy about sharing their biological traits.
Additionally, false positives and negatives are potential pitfalls of biometric authentication systems. These inaccuracies could lock users out or allow unwanted access if misconfigured. Balancing these pros and cons is crucial as organizations consider implementing biometric solutions.
Privacy Concerns and Data Protection
Biometric security offers unparalleled convenience, but it raises serious privacy concerns. The collection of unique biological traits such as fingerprints and facial recognition data poses significant risks.
Once biometric data is captured, it can be challenging to protect. Unlike passwords, you cannot change your fingerprint or retina scan if they are compromised. This permanence makes users vulnerable to identity theft and fraud.
Moreover, how biometric information is stored becomes critical. Many systems do not encrypt this sensitive data adequately, leaving it exposed to breaches. A leak could lead to catastrophic consequences for individuals.
The potential misuse by corporations or governments also stirs unease among consumers. Surveillance technologies could exploit personal data without consent, threatening individual rights and freedoms.
Balancing the benefits of biometric authentication with these privacy issues requires careful consideration from both providers and users alike. Awareness is essential in navigating this complex landscape of biometrics and personal privacy.
Real-world Examples of Biometric Security in Use
Biometric security is making waves across various sectors. Airports have embraced it, allowing travelers to breeze through check-in and boarding processes using facial recognition technology. This not only speeds up travel but enhances safety.
In the corporate world, companies are implementing fingerprint scanners for employee access. This ensures that sensitive areas remain secure while simplifying entry procedures.
Smartphones are another hotbed for biometric authentication. Many users rely on their fingerprints or facial scans to unlock devices and authorize transactions, merging convenience with security seamlessly.
Retailers are also adopting biometrics at checkout points. Customers can use palm vein scanning to pay quickly without cash or cards, creating a frictionless shopping experience.
These examples illustrate how biometric technologies enhance everyday life by offering rapid solutions while addressing modern security challenges.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Biometric security, while convenient, comes with its share of risks. One major vulnerability is the potential for data breaches. Hackers can target biometric databases, stealing sensitive information such as fingerprints or facial scans.
Another concern lies in spoofing. Advanced technology allows criminals to create fake fingerprints or masks that can trick biometric systems. This manipulation raises questions about the reliability of these technologies.
Moreover, once compromised, biometric data cannot be changed like a password. If someone gains access to your biometric profile, it could lead to identity theft and long-lasting consequences.
There’s the issue of misidentification. Biometric authentication systems are not infallible; they can make errors in recognizing individuals under certain conditions. Such inaccuracies may result in unauthorized access or wrongful denial of service.
These vulnerabilities highlight the need for cautious implementation and robust protective measures when utilizing biometric security solutions.
The Future of Biometric Security and Its Impact on Society
As technology continues to evolve, biometric security is poised to become a cornerstone of everyday life. Imagine walking into your home, and the door recognizes you instantly, no keys required. This seamless integration may redefine convenience.
However, with this ease comes a plethora of implications for society. The potential for increased surveillance raises ethical questions about personal freedoms. Are we trading privacy for safety?
Moreover, as biometric authentication systems grow more sophisticated, so do the methods employed by cybercriminals. Society must stay vigilant against these emerging threats while enjoying the benefits of enhanced security.
The acceptance of biometric data in various sectors—finance, healthcare, law enforcement—will shape our interactions profoundly. Will trust be restored in institutions handling sensitive information? This balance will determine if we embrace or resist this technological leap forward.
Balancing Convenience and Risk: Tips for Using Biometric Security Safely
Using biometric security can enhance convenience, but it’s crucial to navigate the associated risks. Start by choosing devices with robust encryption standards. This adds an extra layer of protection to your biometric data.
Regularly update your software and applications. Security patches often contain fixes for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers.
Be mindful of where you store your biometric data. Opt for services that prioritize privacy and offer clear policies on data handling.
Consider using multi-factor authentication whenever possible. Combining biometrics with other forms of verification strengthens overall security.
Stay informed about emerging threats in the realm of biometric privacy. Awareness is key in making educated decisions regarding personal security measures in today’s digital landscape.
Conclusion: Is Biometric Security Worth the Trade-off
As we navigate the complexities of biometric security, it’s essential to weigh its conveniences against potential risks. Biometric authentication offers a level of ease and speed that traditional methods struggle to match. However, with great convenience comes significant responsibility.
The technology continues to evolve rapidly, enabling more secure systems while also raising pressing privacy concerns. The balance between user experience and protecting personal data is delicate. Individuals must consider how much they trust these systems and whether they are prepared for the implications of sharing their biometric data.
Embracing biometric security requires thoughtful consideration of both its advantages and disadvantages. Each user must assess their comfort level with this technology in relation to their personal security needs and values regarding privacy. As society moves forward into an increasingly digital landscape, understanding this trade-off will be key in making informed choices about our identities in the age of biometrics.