Introduction to Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to leverage technology for growth and efficiency. With the rise of data-driven decision-making, two prominent solutions have emerged: edge computing and cloud computing. Each offers unique advantages that can significantly impact how organizations scale operations and manage vast amounts of data.
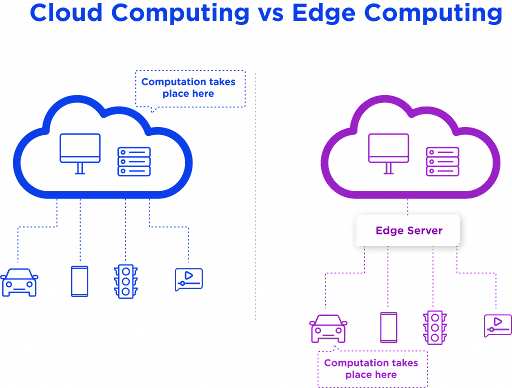
Edge computing brings processing power closer to where it’s needed most—right at the source of data generation. This reduces latency, enhances speed, and supports real-time analytics. On the other hand, cloud computing allows businesses to harness virtually limitless resources over the internet while providing flexibility in managing workloads.
As companies navigate their technological journeys, understanding how these two paradigms differ is crucial for making informed decisions. Which solution is better suited for your organization? Let’s dive into their differences and discover what each has to offer in terms of scalability and performance.
Understanding the Differences Between Edge and Cloud Computing
Edge computing and cloud computing serve different purposes in the technology landscape.
Cloud computing operates on centralized data centers, where vast amounts of information are processed and stored remotely. This model excels in scalability, allowing businesses to access resources as needed without investing heavily in physical infrastructure.
On the other hand, edge computing decentralizes processing power by bringing it closer to the data source. This reduces latency significantly, making it ideal for real-time applications like IoT devices or autonomous vehicles.
While both technologies handle data effectively, their approaches differ markedly. Cloud solutions rely on high-speed internet connections to transmit large volumes of information back and forth. Edge solutions prioritize localized processing to enhance speed and efficiency right at the device level.
Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their operations based on specific needs and use cases within their technology stacks.
Advantages and Limitations of Edge and Cloud Computing
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source. This reduces latency, making it ideal for applications requiring real-time analysis. Businesses can achieve faster response times, crucial in sectors like healthcare and manufacturing. Additionally, edge solutions often consume less bandwidth since they process data locally.
However, edge computing does have its drawbacks. Managing a distributed network of devices poses challenges in maintenance and security. Businesses may need specialized skills to handle these systems effectively.
On the other hand, cloud computing offers scalability and flexibility that many businesses crave. It allows organizations to store vast amounts of data without needing extensive on-premises infrastructure. This model supports collaborative work across different locations seamlessly.
Yet, reliance on an internet connection can be a limitation for cloud services. Outages or slow connections can hinder access to critical data and applications when needed most.
Real-World Applications of Edge and Cloud Computing
Edge computing shines in scenarios demanding real-time data processing. For instance, smart cities leverage edge technology for traffic management. Sensors collect data on traffic flow and adjust lights instantaneously, enhancing efficiency.
In healthcare, wearable devices process patient information at the source. This swift analysis can alert medical professionals to critical changes without delays caused by cloud communication.
Conversely, cloud computing excels with vast storage capabilities. Businesses utilize it for large-scale applications like big data analytics or e-commerce platforms. The ability to access and analyze massive datasets enables firms to derive insights crucial for growth.
Media streaming services also depend heavily on the cloud. They deliver high-quality content globally while managing user demands seamlessly through scalable infrastructure.
Both technologies have unique strengths that cater effectively to distinct industry needs. Choosing wisely based on application requirements is essential for maximizing benefits from each approach.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Business’s Scaling Needs
When it comes to scaling your business, understanding the unique demands of your operations is crucial. Both edge and cloud computing offer distinct advantages tailored for different needs.
If real-time data processing and low latency are priorities, edge computing might be the way forward. It allows for faster decision-making at local levels, which can enhance user experiences significantly.
On the other hand, if you’re looking for vast storage capabilities and flexibility in resources, cloud computing shines. Its ability to scale efficiently without heavy upfront investments can be a game changer for growing businesses.
Consider regulatory compliance as well. Certain industries require stringent data handling protocols that may favor one option over the other.
Assessing factors like budget constraints, required speed of response, and existing technology will guide you toward the right choice for sustainable growth in today’s competitive landscape.
The Future of Edge and Cloud Computing
As we look ahead, the landscape of data processing is evolving rapidly. Edge computing and cloud computing are both set to play crucial roles in shaping how businesses operate. The rise of IoT devices and the demand for real-time data analytics are pushing edge technology into the spotlight. By bringing computation closer to where it’s needed, organizations can reduce latency and improve performance.
On the other hand, cloud computing continues to be a powerhouse for scalability and flexibility. With its ability to provide vast resources on-demand, companies find it indispensable for handling large datasets without significant upfront investment.
The future will likely see a convergence of these technologies rather than an outright competition between them. Hybrid models that leverage both edge and cloud solutions are emerging as powerful strategies for organizations looking to optimize their operations while managing costs effectively.
As advancements in network infrastructure expand capabilities like 5G, expect even greater integration between edge devices and cloud services. This synergy promises not just improved efficiency but also new opportunities across various industries—from healthcare innovations powered by real-time data analysis to smart cities equipped with interconnected systems.
Businesses must keep an eye on these developments as they navigate their own scaling needs within this changing technological landscape. Embracing both edge and cloud solutions could very well lead to enhanced operational agility, better customer experiences, and ultimately—sustained growth in today’s competitive environment.