Introduction to Arthritis
Arthritis affects millions of people worldwide, making it a common yet often misunderstood condition. It’s not just an old person’s ailment; individuals of all ages can experience its effects. From joint pain to inflammation, arthritis presents various challenges that can impact daily life in significant ways. Understanding this health issue is crucial for managing symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
Whether you’re seeking relief or trying to support someone who suffers from arthritis, knowing the basics is essential. This guide will navigate through the symptoms, types, causes, treatment options, and lifestyle changes associated with arthritis—equipping you with valuable knowledge on how to tackle this chronic condition head-on. Let’s delve deeper into what arthritis really means and explore effective ways to cope with its impacts.
Common Symptoms of Arthritis
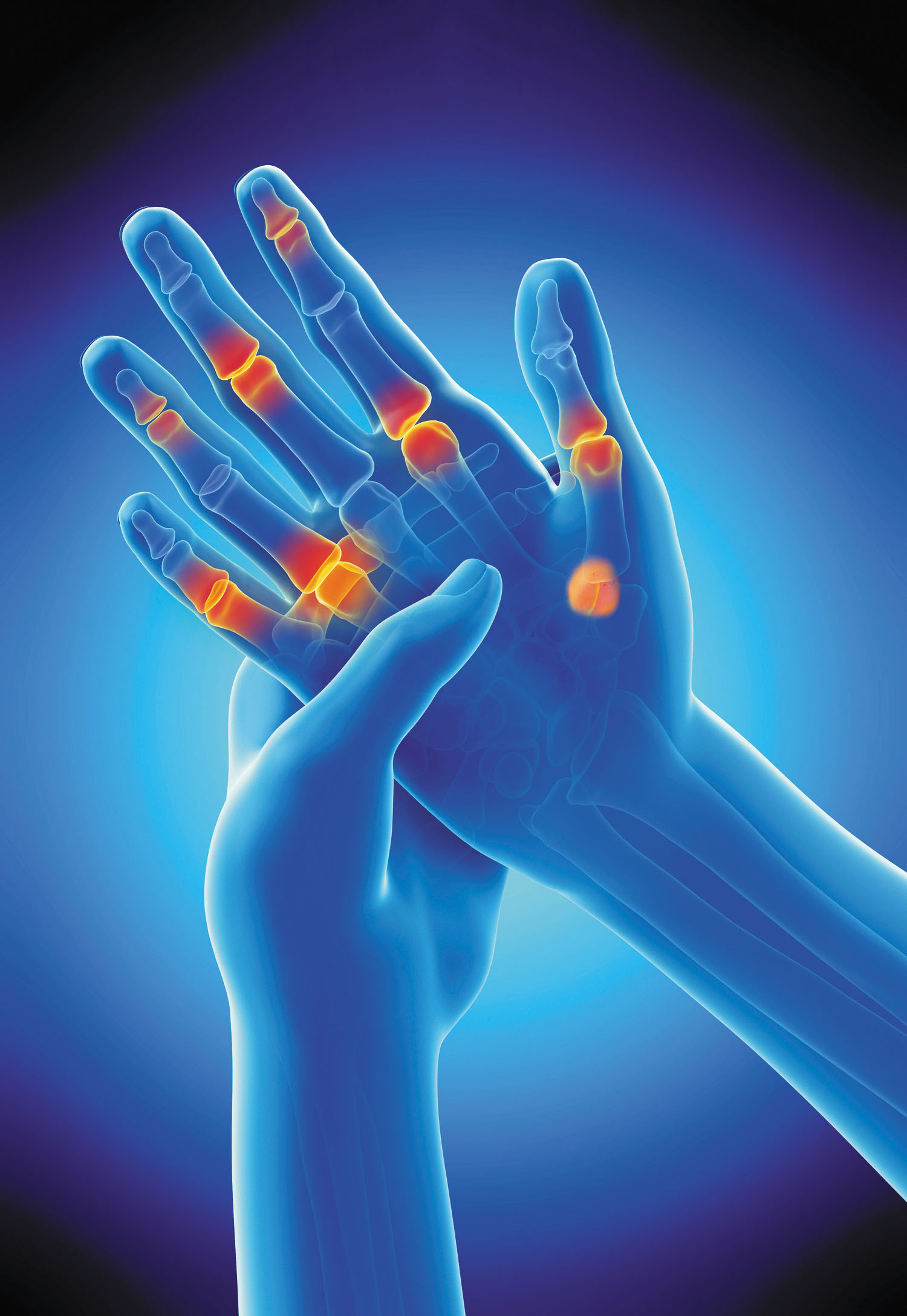
Arthritis manifests through a variety of symptoms that can significantly affect daily life. Joint pain is often the first noticeable sign, ranging from mild discomfort to debilitating agony.
Swelling around joints may also occur, leading to visible inflammation. This swelling can make movement challenging and uncomfortable.
Stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity, is another hallmark symptom. Many people find it difficult to get moving at times when they need flexibility most.
Fatigue is common too; chronic pain can drain energy levels significantly.
Some individuals experience reduced range of motion in affected joints over time. These symptoms collectively indicate a need for timely evaluation and treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Different Types of Arthritis and Their Causes
Arthritis is not a single condition; it encompasses over 100 different types. Each type has its own unique causes and symptoms.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form, often resulting from wear and tear on joints over time. It’s frequently associated with aging but can also stem from previous injuries or obesity.
Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks joint tissues. Genetics and environmental factors might trigger this response.
Psoriatic arthritis links directly to psoriasis, a skin condition. It develops when inflammation affects both skin and joints due to immune system dysfunction.
Gout arises from excess uric acid in the blood, leading to sharp crystal formations in joints. Diet plays a significant role in its onset.
These diverse forms of arthritis highlight how varied their origins can be, emphasizing that understanding your specific type is crucial for effective management and treatment options.
Risk Factors for Developing Arthritis
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing arthritis. Age is a significant contributor; as people get older, their joints undergo wear and tear.
Genetics also play a role. If someone has family members with arthritis, they may be at greater risk too.
Gender matters as well. Studies indicate that women are more likely to develop certain types of arthritis compared to men, especially rheumatoid arthritis.
Obesity adds extra stress to weight-bearing joints like knees and hips. This added pressure can lead to earlier onset of conditions such as osteoarthritis.
Previous joint injuries from sports or accidents can set the stage for future problems in those same areas.
Lifestyle choices shouldn’t be overlooked either. A lack of physical activity can weaken muscles around joints, making them susceptible to injury and pain over time.
Treatment Options for Arthritis
When it comes to treating arthritis, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Various options cater to individual needs and preferences.
Medications play a crucial role in managing symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. For some, corticosteroids offer quick relief during flare-ups.
Physical therapy is another effective method. A skilled therapist can create tailored exercises that improve mobility and strength without straining the joints.
For those seeking advanced treatments, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may slow progression in certain types of arthritis, especially rheumatoid arthritis.
Surgical interventions like joint replacement are considered when conservative methods fail to provide relief or restore function effectively.
Complementary therapies such as acupuncture can also be beneficial for many individuals looking for holistic treatment pathways. Each option has its place depending on severity and personal circumstances.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Arthritis Symptoms
Managing arthritis symptoms often begins with small changes in daily life. Incorporating gentle exercises, such as swimming or yoga, can improve flexibility and reduce stiffness. Movement is essential; even short walks can make a significant difference.
Diet also plays a crucial role in symptom management. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods—like leafy greens, nuts, and fatty fish—can help alleviate discomfort. Staying hydrated is equally important.
Adequate sleep supports recovery and overall well-being. Establishing a consistent sleep routine can enhance rest quality.
Social connections shouldn’t be overlooked either. Engaging with friends or support groups fosters emotional health while sharing experiences helps lighten the burden of living with arthritis.
Mindfulness practices like meditation may provide mental clarity and peace amidst physical challenges. These lifestyle shifts collectively empower individuals to take control over their symptoms effectively.
Alternative Therapies for Arthritis Relief
Alternative therapies can offer valuable support for those managing arthritis. Many individuals turn to acupuncture, which may help reduce pain and improve mobility by targeting specific points in the body.
Another option is massage therapy. Gentle manipulation of muscles and joints can promote relaxation, ease stiffness, and enhance overall well-being.
Herbal remedies also play a significant role in alternative treatments. Turmeric, with its anti-inflammatory properties, has gained popularity among arthritis sufferers seeking natural relief.
Mind-body practices like yoga or tai chi combine gentle movement with mindfulness. These approaches not only assist physical function but also foster mental clarity and emotional balance.
Dietary changes may provide benefits too. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids found in fish or walnuts can potentially decrease inflammation over time. Each person’s response varies; exploring these options could lead to finding what works best for you.
Coping with the Emotional Impact of Arthritis
Living with arthritis can take a toll on your emotional well-being. The constant pain and limitations may lead to feelings of frustration, sadness, or even isolation.
It’s essential to acknowledge these emotions rather than suppress them. Talking openly about your feelings with friends, family, or support groups can provide relief and understanding.
Engaging in mindfulness practices like meditation or yoga might also help you manage stress. These techniques foster a sense of calm that counters anxiety related to chronic pain.
Consider seeking professional help if you’re struggling emotionally. A therapist specialized in chronic illness can offer valuable coping strategies tailored for your situation.
Remember that it’s okay to ask for help when needed—whether it’s from loved ones or healthcare providers. Building a strong support network is crucial in navigating the emotional landscape of living with arthritis.
Prevention Tips to Reduce the Risk of Developing Arthritis
Preventing arthritis involves a proactive approach to your overall health. Staying active is crucial; regular exercise helps maintain joint function and reduces stiffness. Aim for activities that are easy on the joints, such as swimming or cycling.
Maintaining a healthy weight also plays a significant role in preventing arthritis. Extra weight puts additional stress on your joints, particularly those in the lower body. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help too. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids found in fish.
Staying hydrated is essential for joint lubrication. Make it a habit to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can further protect your joint health.
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals allow you to monitor any risk factors early on. They can provide tailored advice suited to your specific needs and lifestyle choices.
By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing arthritis while enhancing your overall well-being.