Introduction to Biometric Security
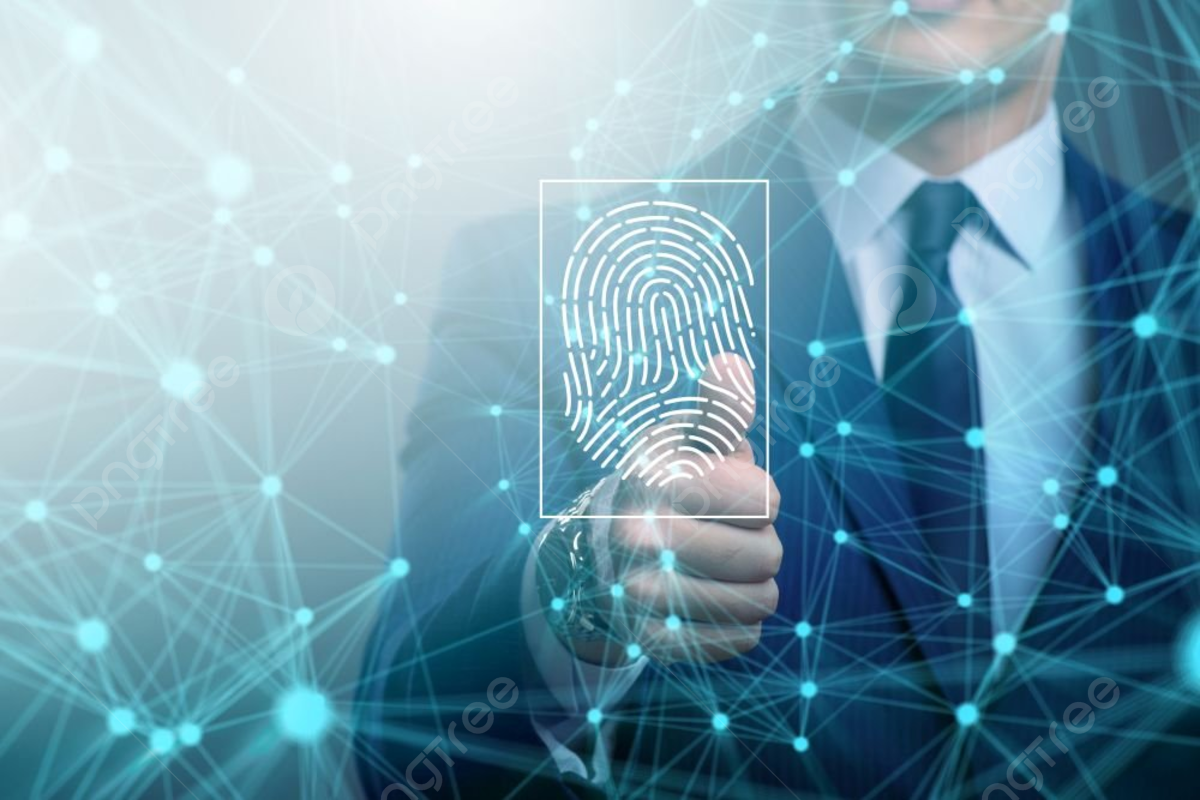
In a world where security breaches are increasingly common, the need for robust protection has never been more pressing. Traditional methods, like fingerprints and facial recognition, have served us well but often fall short in ensuring our data remains safe from prying eyes. As technology evolves, so too does the way we think about biometric security. Enter the fascinating realms of heartbeats and brainwaves—two unique identifiers that could revolutionize how we protect our digital lives.
Imagine a future where your heartbeat is not just a measure of health but also an essential key to accessing sensitive information. Picture being authenticated by your own brainwave patterns as you enter secure spaces or unlock devices. These advancements promise not only enhanced security but also greater convenience in our interconnected world.
This blog post delves into these exciting developments within biometric technology, exploring how they can reshape our approach to identity verification while addressing critical concerns around privacy and reliability. Let’s embark on this journey into the next frontier of biometric security beyond fingerprints!
Traditional Biometric Methods (Fingerprints, Facial Recognition, etc.)
Traditional biometric methods have long been the cornerstone of secure identification. Fingerprints, with their unique patterns, offer a reliable way to verify identity. This method has been widely adopted in various applications, from unlocking smartphones to securing access points.
Facial recognition technology is another popular option. It analyzes facial features and compares them against stored images. Many people encounter this daily through social media tagging or airport security checks.
Iris scanning also deserves mention for its precision. The intricate patterns in our irises are as unique as fingerprints and can provide high levels of security.
While these technologies have proven effective over time, they come with limitations and vulnerabilities that hackers continuously seek to exploit. As we advance into a more digital world, the need for innovative solutions grows increasingly urgent.
Advancements in Biometric Technology: Heartbeats and Brainwaves
Biometric technology is undergoing a remarkable evolution. Traditional methods like fingerprints and facial recognition are being complemented by innovative approaches: heartbeats and brainwaves.
Heartbeats, unique to every individual, can be measured using wearable devices. These tools capture the electrical signals produced by the heart, providing an additional layer of security. This method not only identifies users but also tracks their emotional states in real-time.
Brainwave biometrics take it a step further. By analyzing patterns from electroencephalogram (EEG) readings, systems can authenticate users based on specific mental states or thoughts. This technology holds potential for secure access across various platforms.
These advancements pave the way for more personalized and adaptive security measures, moving beyond traditional biometric methods to enhance user experience while ensuring safety. As research continues, we may see even broader applications in fields ranging from finance to healthcare.
How Heartbeats and Brainwaves Can Be Used for Security
Heartbeats and brainwaves offer a fascinating frontier in biometric security. Unlike traditional methods, these physiological signals are unique to each individual, making them difficult to replicate.
Heart rhythms fluctuate based on emotional states and stress levels. This variability can serve as an authentication method. By analyzing heartbeat patterns, systems can distinguish between authorized users and potential intruders.
Brainwave biometrics takes it a step further by measuring electrical activity in the brain. EEG devices capture these signals, which are influenced by cognitive processes. Patterns linked to specific thoughts or actions could create secure access points for sensitive data.
Using heartbeats and brainwaves introduces dynamic layers of protection that evolve with the user’s biological state. As technology advances, integrating this type of behavioral biometrics promises more resilient defenses against unauthorized access.
Benefits of Using Heartbeats and Brainwaves for Biometric Security
Heartbeats and brainwaves offer a unique layer of security that goes beyond traditional methods. Unlike fingerprints or facial recognition, these biometric indicators are much harder to replicate or forge.
The dynamic nature of heartbeats means they change based on emotional states and physical conditions. This variability adds an extra dimension to security measures, making it difficult for unauthorized users to mimic someone else’s heartbeat pattern.
Brainwave biometrics tap into the electrical activity in our brains. Each person has distinct brainwave patterns, which can serve as a highly personalized authentication method. This makes it incredibly difficult for anyone other than the authorized user to gain access.
Moreover, these technologies enhance user convenience. They can be seamlessly integrated into daily activities without requiring additional steps like scanning a fingerprint or entering passwords. The potential for continuous monitoring also opens doors for real-time authentication in various applications.
Potential Concerns and Limitations
As promising as biometric security through heartbeats and brainwaves may be, it comes with its share of concerns. One major issue is the accuracy of biometric data collection. Variations in individual physiology can lead to false positives or negatives, undermining trust in these systems.
Privacy remains a significant concern. Collecting sensitive biometric data raises questions about how this information will be stored and used. Users might worry that their personal data could fall into the wrong hands.
There’s also the challenge of technological integration. Many existing systems are designed for traditional biometrics like fingerprints. Transitioning to more advanced methods requires time, investment, and training.
Public acceptance plays a vital role in adoption rates. Some individuals may feel uneasy about using brainwave biometrics or heartbeat recognition due to misconceptions around surveillance and control over their personal space.
Future of Biometric Security Beyond Fingerprints
The future of biometric security is evolving rapidly, moving well beyond traditional methods like fingerprints. As technology advances, we’re seeing a shift towards more dynamic forms of identification that account for individual behaviors and physiological traits.
Heartbeats, with their unique patterns and rhythms, offer a promising avenue. Devices can detect these subtle variations in real-time, allowing for seamless verification without direct interaction.
Brainwave biometrics also present an intriguing possibility. By analyzing brain activity through EEG sensors, systems could authenticate users based on cognitive states or emotional responses. This level of personalization opens doors to enhanced security measures tailored to each user’s neural signature.
As society increasingly embraces digital interactions, the demand for robust solutions will drive innovation in behavioral biometrics. The integration of these technologies could provide not only higher accuracy but also a more intuitive experience across various platforms.
Conclusion
The landscape of biometric security is evolving rapidly. As technology advances, we must embrace new methods that offer improved accuracy and convenience. Heartbeats and brainwaves represent a frontier in biometric applications that could redefine how we approach personal identification.
With the rise of behavioral biometrics, these innovative techniques provide a deeper layer of security beyond traditional measures like fingerprints or facial recognition. The potential to harness unique physiological data underscores the move toward more personalized and secure authentication processes.
However, this shift also brings forth important discussions around biometric data privacy. It’s essential to consider ethical implications as we integrate such sensitive information into our security frameworks.
As research progresses, heart-based and brainwave biometrics might become standard practice across various sectors—from banking to healthcare—enabling seamless interactions while enhancing safety protocols.
Adopting these technologies may require adjustments in regulations and user education on safeguarding their biometric identity. The future holds much promise for developing robust systems that prioritize both functionality and privacy in an increasingly digital world where securing personal information remains paramount.